What is the Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS

In the digital age, ensuring the security of websites and protecting user data has become more important than ever. This is where HTTPS comes into play.
If you’ve ever noticed a small padlock icon in your web browser’s address bar or seen a website’s URL start with “https://,” you’ve encountered HTTPS. In modern web browsers such as Chrome, websites that do not use HTTPS are marked differently than those that are. But what exactly is HTTPS, and how does it differ from plain HTTP?
This comprehensive guide will explore Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), how it works, and why it is crucial for websites today. We will also discuss the benefits of HTTPS for website owners and how it impacts search engine optimization (SEO).
We’ll also introduce you to LinkLumin, a company dedicated to helping businesses secure their online presence with HTTPS and other digital security solutions.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a business owner new to the web, this post will help you understand the importance of HTTPS and how to implement it effectively.
Table of Contents
- What Is HTTPS?
- How Does HTTPS Work?
- The Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Why Is HTTPS Important for Websites?
- How to Enable HTTPS on Your Website
- Common HTTPS Myths and Misconceptions
- Troubleshooting Common HTTPS Issues
- How LinkLumin Can Help Secure Your Website with HTTPS
- What Is HTTPS?
HTTPS is the abbreviation for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, an extension of the HTTP protocol used for secure communication over the Internet.
While HTTP is the standard protocol for transferring data between a web server and a client (such as web browsers), HTTPS adds a layer of security to the HTTP connection by encrypting the data.
This ensures that any information exchanged between the server and the client, such as login credentials or payment details, is protected from unauthorized access.
Key Features of HTTPS Websites:
- Encryption: HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between the web server and the web browsers using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
- Data Integrity: HTTPS ensures that data is not corrupted during transfer and has not been altered by third parties.
- Authentication: It verifies that the website you are communicating with is the one you intend to access, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
How HTTPS Works in a Nutshell:
When you visit HTTPS websites, your browser and the web server perform a secure “handshake” using a digital certificate issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). This handshake establishes a secure connection between web servers where data can be safely exchanged.
How Does HTTPS Work?
HTTPS relies on a combination of two key technologies: encryption and authentication. Together, they ensure that any data sent over an HTTPS connection is secure and authentic.
The Process of HTTPS:
- Connection Initiation: When a user navigates to an HTTPS website, the web browser requests that the web server initiate a secure connection.
- Certificate Exchange: The server responds by sending its SSL/TLS certificate, which contains the server’s public key.
- Certificate Verification: The browser checks the certificate against its list of trusted CAs. If the certificate is valid, the browser proceeds to the next step.
- Key Exchange: The browser and server agree on a symmetric encryption key using the public and private keys. This key encrypts and decrypts the data exchanged during the session.
- Secure Data Transfer: Once the secure connection is established, the browser and server can exchange encrypted data, ensuring that any information transferred is protected from eavesdropping.
The Role of SSL/TLS Certificates:
An SSL/TLS certificate is a digital certificate issued by a Certificate Authority that verifies a website’s identity. It contains information about the certificate’s validity, the domain name, and the server’s public and private key used. This certificate is crucial for establishing a secure HTTPS connection.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates:
- Domain Validated (DV): Verifies only the ownership of the domain.
- Organization Validated (OV): Confirms the domain ownership and organization identity.
- Extended Validation (EV): Provides the highest level of validation, displaying the company name in the browser’s address bar.
These certificates provide varying levels of assurance to users and are essential for building trust in your website.
The Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
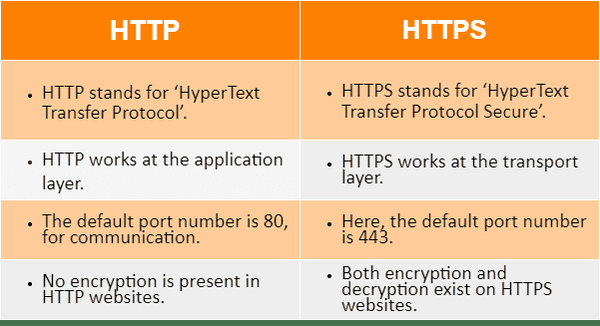
The primary difference between HTTP and HTTPS lies in the security features provided by HTTPS. While HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which is used for data exchange over the most modern web browsers, HTTPS adds a layer of security through SSL/TLS encryption.
Key Differences:
- Security:
- HTTP: Data is transferred in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and tampering.
- HTTPS: Data is encrypted, protecting it from unauthorized access and ensuring its integrity.
- Authentication:
- HTTP: This does not verify the server’s identity, leaving users susceptible to phishing attacks.
- HTTPS: Uses a digital certificate to verify the server’s identity, ensuring that users are connected to the intended website.
- SEO Impact:
- HTTP: Not favored by search engines like Google, which may lower the site’s ranking.
- HTTPS: Preferred by search engines, as it indicates a secure and trustworthy website. This can positively impact your site’s SEO performance. malicious root certificate secure connections
How HTTPS Impacts User Experience:
When users visit an HTTPS website, they see a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection. This visual cue assures users that their data is protected, builds trust, and encourages them to interact with the site.
Browser Behavior for HTTP vs. HTTPS:
Modern browsers like Google Chrome and Firefox display HTTP warnings for sites, marking them as “Not Secure.” This can deter users from visiting your site or sharing sensitive information.
In contrast, major browsers and HTTPS sites are marked as secure, providing a better user experience and increased trust.
Why Is HTTPS Important for Websites?
Implementing HTTPS on your website is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
The migration to HTTPS has significantly enhanced the security of all data exchanged, despite the fact that a hacker can still potentially access IP addresses, port numbers, domain names, the quantity of information exchanged, and the duration of a session.
Here’s why:
Protects Sensitive Data:
HTTPS encrypts data transferred between the client computer and the server, protecting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details from interception and misuse.
Improves SEO:
Search engines like Google prioritize HTTPS websites in their rankings. This means HTTPS can give you an edge over competitors who are still using HTTP.
Builds User Trust:
A website with a secure connection symbol (the padlock icon) reassures users that their data is safe. This is particularly important for e-commerce sites and sites that handle sensitive user data.
Compliance with Industry Standards:
Many industries require HTTPS to comply with data protection regulations. For instance, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates that websites that process credit card transactions utilize HTTPS.
Prevents Content Injection:
HTTPS prevents third parties from injecting unwanted content into your website, such as ads or malware. This ensures that users see the content as you intended.
For these reasons, enabling HTTPS is crucial for website owners who want to protect their users and maintain a professional, secure version and trustworthy online presence.
How to Enable HTTPS on Your Website
Enabling HTTPS on your website involves several steps, including obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate and configuring your server to support HTTPS connections.
Step-by-Step Guide to Enabling HTTPS:
- Choose an SSL/TLS Certificate: Based on your site’s requirements, decide on the type of certificate you need. For most websites, a Domain Validated (DV) certificate will suffice. For e-commerce or high-security sites, consider an EV certificate.
- Purchase and Install the Certificate: Obtain the certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority or your hosting provider. Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through services like Let’s Encrypt.
- Configure Your Web Server: Update your web server settings to enable HTTPS. This involves configuring the server to use the SSL/TLS certificate and redirecting HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
- Update Your Website URLs: Change all internal links, images, and scripts to HTTPS. This prevents mixed content issues, where some elements of your site are still loaded over HTTP.
- Test the Configuration: Use tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to verify that your HTTPS configuration is correct and secure.
- Update Search Console: Add your new HTTPS site to Google Search Console to ensure that Google indexes your HTTPS pages correctly.
Switching from HTTP to HTTPS:
If your hosting provider offers an automated SSL setup, you can switch your site from HTTP to HTTPS with just a few clicks.
However, to avoid mixed content warnings, you must ensure that all resources (images, scripts, etc.) are served over HTTPS.
Maintaining Your HTTPS Site:
- Renew Your SSL Certificate: SSL certificates have an expiration date, typically ranging from one to three years. Set reminders to renew your certificate before it expires to avoid security warnings.
- Monitor for Issues: Regularly check for mixed content and configuration issues that could compromise your site’s security.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Protect your site and hosting account with two-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
Common HTTPS Myths and Misconceptions
Despite its widespread adoption, several myths and misconceptions about HTTPS persist. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones.
Myth 1: HTTPS Is Only Necessary for E-Commerce Sites
Fact: While HTTPS is essential for sites that handle sensitive data, such as payment information, it’s also important for all websites to protect user data and ensure privacy.
Myth 2: HTTPS Slows Down Websites & Web Browsers
Fact: Modern implementations of HTTPS, using HTTP/2 and optimized SSL/TLS configurations, can improve website performance compared to HTTP connections.
Myth 3: HTTPS Is Expensive
Fact: While paid SSL certificates exist, many hosting providers offer free options through Let’s Encrypt. These certificates provide the same level of encryption as paid certificates.
Myth 4: HTTPS Guarantees 100% Security
Fact: While HTTPS encrypts data in transit, it does not protect against all types of attacks, such as phishing or malware. Additional security measures are still necessary.
Myth 5: Once Implemented, HTTPS Doesn’t Need Maintenance
Fact: HTTPS requires regular maintenance, including renewing your SSL certificate and checking for configuration issues. Regular audits help ensure your site remains secure.
Understanding these facts can help you make informed decisions about implementing and maintaining HTTPS on your website.
Troubleshooting Common HTTPS Issues
Implementing HTTPS can sometimes lead to issues that must be addressed to ensure a smooth, secure user experience.
Common HTTPS Issues and Solutions:
- Mixed Content Warnings:
- Issue: Some resources (images, scripts, etc.) are still being loaded over HTTP.
- Solution: Update all resource URLs to use HTTPS.
- Expired SSL Certificates:
- Issue: An expired certificate will trigger a security warning in browsers.
- Solution: Renew the certificate before it expires and install the new one on your server.
- SSL/TLS Configuration Errors:
- Issue: Misconfigurations can prevent your site from being properly secured.
- Solution: Use an SSL checker tool to identify and fix configuration issues.
- Browser Security Warnings:
- Issue: Browsers may display warnings if the certificate is not trusted or has configuration errors.
- Solution: Ensure a trusted CA issues your certificate and that it matches your domain name.
- Redirect Loops:
- Issue: Incorrectly configured redirects can cause an infinite loop, preventing access to your site.
- Solution: Check your .htaccess file or server configuration to ensure that redirects are correctly set up.
Tips for Ongoing HTTPS Maintenance:
- Regular Audits: Perform security audits to check for vulnerabilities and configuration issues.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest SSL/TLS technology developments and best practices.
- Use Monitoring Tools: Utilize tools like SSL Labs and security plugins to monitor your site’s HTTPS status and receive alerts for any issues.
- How LinkLumin Can Help Secure Your Website with HTTPS
At LinkLumin, we understand that securing your website with HTTPS is a crucial step in building trust and credibility online.
Our team of experts is dedicated to helping businesses easily implement and maintain HTTPS, ensuring that their sites remain secure and accessible to users.
Our HTTPS Services Include:
- SSL/TLS Certificate Selection and Installation: We help you choose the right SSL/TLS certificate for your site, whether you need a standard DV certificate or a premium EV certificate for added assurance.
- HTTPS Configuration and Optimization: Our team configures your web server to support HTTPS, ensuring optimal performance and security.
- Migration from HTTP to HTTPS: We handle the entire migration process, from updating URLs to configuring redirects and testing your site for any issues.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Support: We continuously monitor your SSL/TLS certificate and HTTPS configuration, alerting you to any issues and ensuring your site remains secure.
- Advanced Security Solutions: We offer additional services, such as two-factor authentication, intrusion detection, and malware scanning, for businesses with more complex security needs.
Why Choose LinkLumin?
Expertise: Our team has extensive experience implementing HTTPS for websites of all sizes and industries.
Comprehensive Support: We offer end-to-end support, from selecting the right certificate to ongoing maintenance and security monitoring.
Customer-focused: We work closely with you to understand your unique needs and ensure your website is fully secured and optimized.
With LinkLumin, you can be confident that your website is secure and provides a seamless and trustworthy user experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) and implementing it on your website is essential for protecting user data, building trust, and improving your search engine rankings.
HTTPS is no longer an option but necessary for any website owner who values security and user experience.
Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can enable HTTPS on your site and enjoy its many benefits, from enhanced security to better SEO.
If you need help securing your website, LinkLumin is here to assist you with our comprehensive range of HTTPS and digital security services.
Ready to secure your website with HTTPS? Contact LinkLumin today to learn how we can help you protect your online presence and provide your users with a secure, trustworthy experience.
Tags
- Thunder Bay
- Content
- Backlinks
- Backlinks Off Page
- website Design
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Benchmark Website Performance
- Off page SEO
- Link Building
- Web
- Keywords
- SEO Services in Mississauga
- Webdesign
- web development
- Digital Marketing
- technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Websites
- Brampton SEO
- Website
- Ecommerce
- Email Marketing
- mobile local SEO
- Web Design
- Local SEO
- Google ADS
- Seo




